Undergraduate Programs (BEng)
Ìı
Student Testimonials
Recent undergraduate students share their Industrial Engineering experiences.
Applying to HÂş»
Prospective students interested in Industrial Engineering at HÂş» will apply to theÌıgeneral undergraduate Bachelor of EngineeringÌıprogram.
Students who have completed theÌıAssociated University ProgramÌımust also submit anÌıofficial transcriptÌıof yourÌıassociated university academic recordÌıverifying completion of the program entrance requirementsÌıto the RegistrarÌıby the date shown on the application form.
A Career in Industrial Engineering
Industrial Engineers optimize processes and systems by finding ways to save time, money, energy, and materials. Through mathematical models, Industrial Engineers design systems and methods that will help businesses meet their production goals. Whether it's streamlining the manufacturing processes of automobiles to make cars more affordable or optimizing the nursing staff at a hospital to improve patient care, career options span a range of industries.
Ìı
Ìı
What you'll learn/do with a BEng degreeÌıin Industrial Engineering
The Faculty of Engineering at HÂş» provides aÌıwell-balanced technical education.
HÂş»'s Engineering Diploma program (Years 1 and 2)

Ìı
You can begin your studies at HÂş» or if you prefer to begin your studies in a smaller campus environment, the Engineering Diploma program at HÂş»'s Faculty of Agriculture in Truro is the academic equivalent of the first two years of an Engineering degree (BEng). After earning your diploma, you can complete the final two or three years of your BEng in Halifax.
Questions?
Years 1 & 2
Faculty of Engineering - Undergraduate Studies Office
Email:Ìıengineering@dal.ca
Phone: 902-494-2082
Ìı
A substantial part of the work in first and second year is made up ofÌıcore classesÌıcommon to all engineering disciplines. You willÌıapply to your preferred disciplineÌıin the winter term of first year and the elective classes taken in second year will depend on your selected discipline.
Ìı
TheÌıfirst and second yearsÌı(Study Terms 1, 2, 3, and 4) of study areÌıcommonÌıtoÌıall engineering students. You will choose to focus on a specific engineering discipline in yourÌıthird yearÌıof study.Ìı.
Applying to an engineering discipline
In the winter term of your first year, you will apply to the Industrial Engineering discipline. See the For Current Students section for more information onÌıapplying to an engineering discipline.
Program Curriculum
You may choose to complete the 5-year Co-op Program or the 5-year Standard Non Co-op Program. Co-op students take theÌısame academic programÌıas the non co-op program; however, our co-op option gives you an opportunity to complement your studies withÌıthree paid work terms.
Accelerated non co-op students take the same academic program as the co-op students; however, Study Term 6 would be taken before Study Term 5.
* Note: Please email ieng@dal.ca no later than January to receive advice and permission to join the accelerated non co-op program in May.
Learn more about each option:
You'll gain real life experience
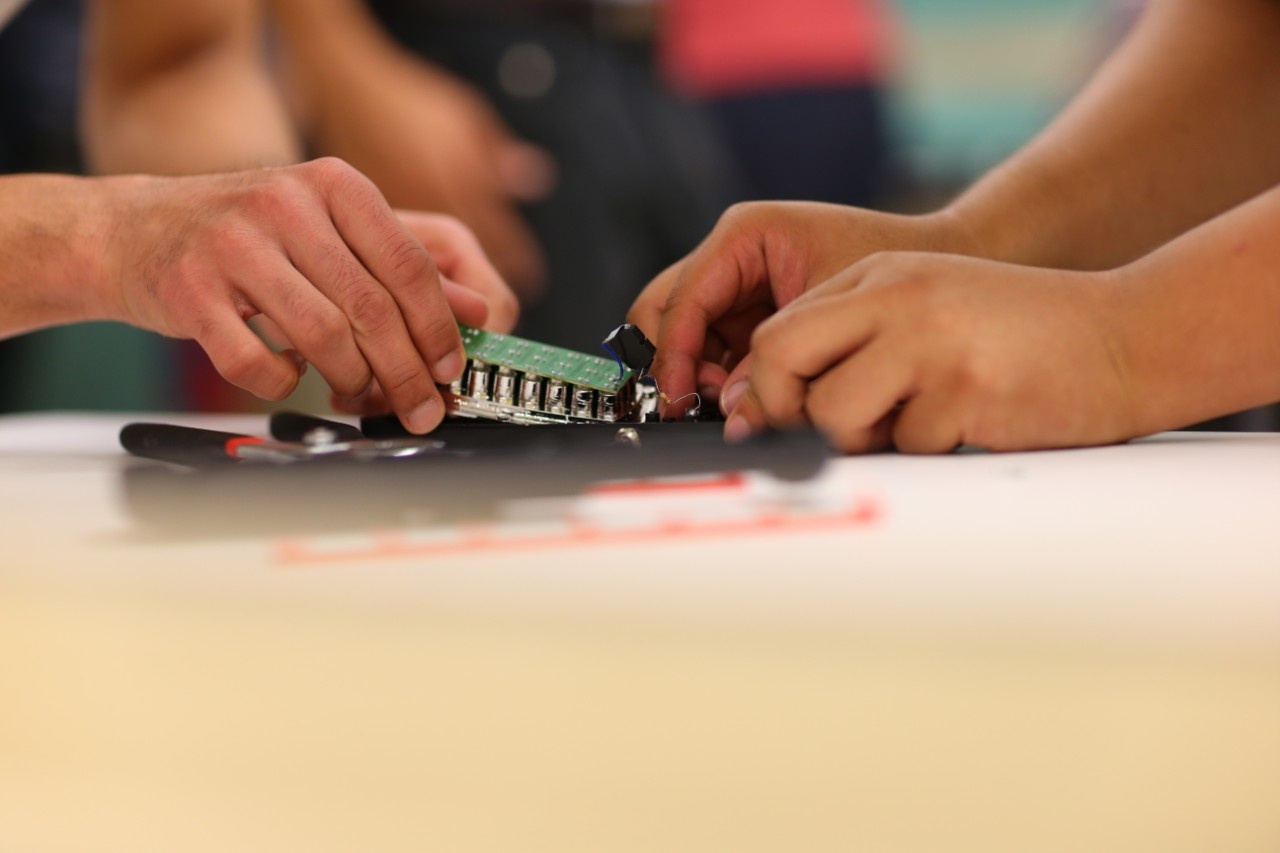
In their final year,Ìıall students undertake a major project. Projects are drawn from companies or institutions outside the University and are treated as a consulting assignment.
The students are evaluated based on their ability to achieve an innovative solution by drawing upon the analytical skills developed throughout their program of studies. They must also, of course, satisfy the practical requirements of the outside client.
